Treatment for dizziness caused by inner ear – Dizziness caused by inner ear issues can be a debilitating condition, affecting balance and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide delves into the medical conditions, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications associated with inner ear dizziness, empowering you with the knowledge and strategies to regain your equilibrium.
As we navigate the complexities of inner ear dizziness, we will explore the underlying causes, diagnostic tools, and effective treatment approaches. Together, we will unlock a path towards improved balance and reduced symptoms, restoring your quality of life.
Medical Conditions Associated with Inner Ear Dizziness
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/causes-of-vertigo-1298945-color-V13-614e9f9446fe4596bd4180958509cc61.png)
Dizziness caused by inner ear problems can result from various medical conditions that affect the vestibular system, the part of the inner ear responsible for balance and spatial orientation. These conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the vestibular system, leading to dizziness, vertigo, and other balance-related symptoms.
Common medical conditions associated with inner ear dizziness include:
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
BPPV is a common cause of brief episodes of dizziness triggered by specific head movements, such as rolling over in bed or looking up. It occurs when tiny calcium crystals (otoconia) in the inner ear become dislodged and move into the fluid-filled canals of the vestibular system.
These crystals can interfere with the normal flow of fluid in the canals, causing dizziness.
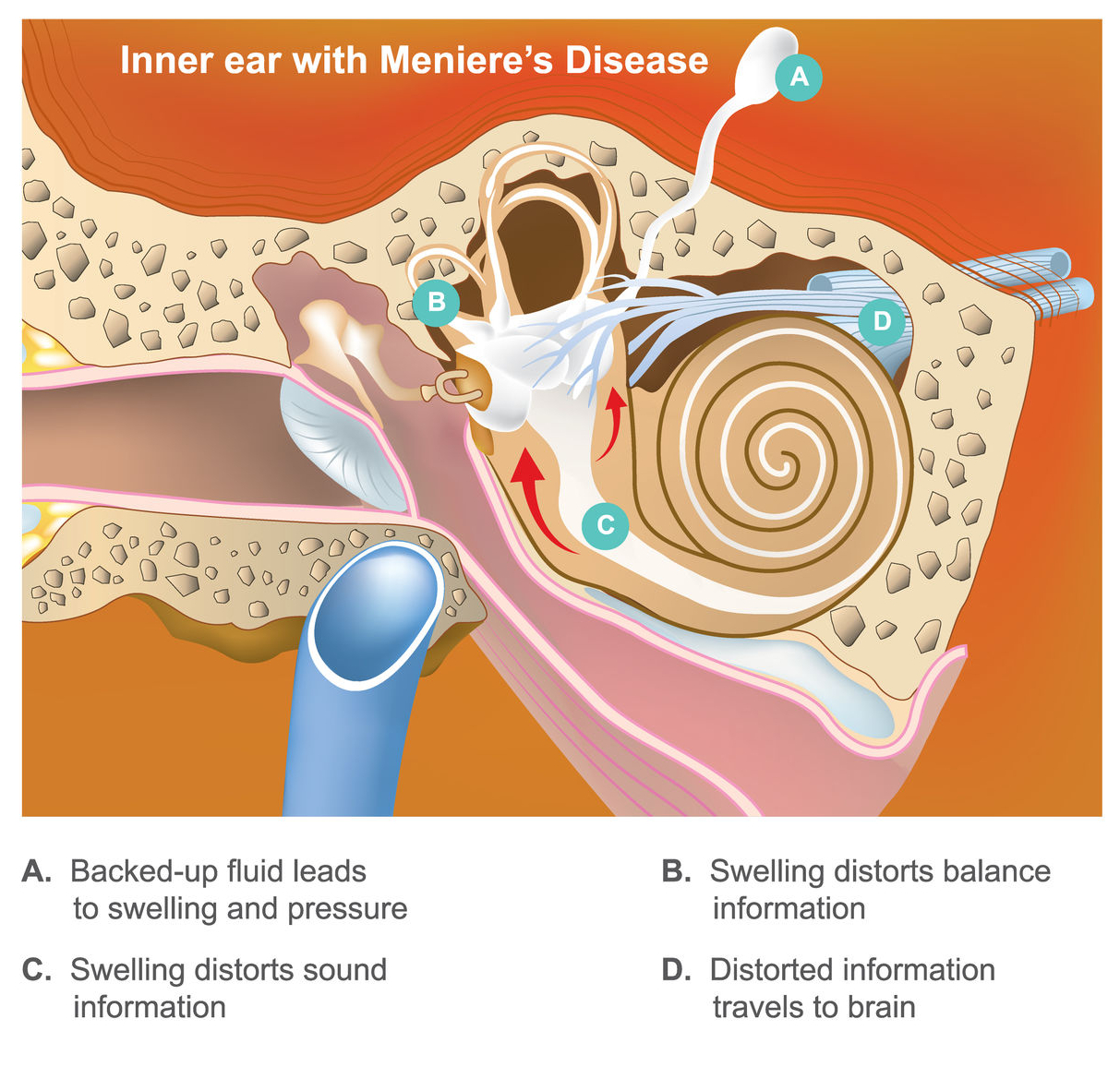
Ménière’s Disease
Ménière’s disease is a chronic condition that affects the inner ear and can cause episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. It is thought to be caused by a buildup of fluid in the inner ear, which can put pressure on the delicate structures of the vestibular system.
Vestibular Neuritis
Vestibular neuritis is an inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain. It can cause sudden onset of severe dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. The inflammation can disrupt the signals sent from the inner ear to the brain, leading to balance problems and dizziness.
Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the inner ear labyrinth, which contains the vestibular system and the cochlea (the organ of hearing). It can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection and can lead to dizziness, hearing loss, and tinnitus.
The inflammation can damage the delicate structures of the inner ear, affecting balance and hearing.
Acoustic Neuroma
An acoustic neuroma is a non-cancerous tumor that grows on the vestibular nerve. It can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness as it grows and puts pressure on the nerve. In severe cases, it can also lead to facial weakness and numbness.
Diagnostic Procedures for Inner Ear Dizziness
Evaluating dizziness caused by inner ear issues involves a comprehensive examination and diagnostic tests. These tests help identify the underlying cause of the dizziness and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Physical Examination
The physical examination includes a detailed assessment of the ears, head, and neurological system. The doctor may check for nystagmus (involuntary eye movements), hearing loss, and balance problems. They may also perform a Dix-Hallpike maneuver to assess for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
Audiometry, Treatment for dizziness caused by inner ear
Audiometry is a test that evaluates hearing function. It can detect hearing loss, which may be a symptom of an underlying inner ear disorder.
Vestibular Function Tests
Vestibular function tests assess the balance system. These tests may include:
- Electronystagmography (ENG):Records eye movements in response to head movements and caloric stimulation.
- Videonystagmography (VNG):Similar to ENG but uses video recordings to capture eye movements.
- Rotary chair test:Measures the body’s response to rotation.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies can visualize the inner ear and surrounding structures. These studies may include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):Creates detailed images of the brain and inner ear.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan:Provides cross-sectional images of the skull and inner ear.
Accuracy and Limitations
The accuracy of diagnostic procedures for inner ear dizziness varies depending on the test and the underlying cause. Some tests, such as audiometry, are highly accurate in detecting hearing loss. Others, such as ENG, may have limitations in differentiating between different inner ear disorders.
Treatment Options for Inner Ear Dizziness
Inner ear dizziness can be a debilitating condition, but there are a variety of treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and improve balance.
The choice of treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the dizziness, as well as the severity of the symptoms.
Vestibular Rehabilitation
Vestibular rehabilitation is a type of physical therapy that is designed to help improve balance and reduce dizziness.
Vestibular rehabilitation exercises can include:
- Eye exercises to improve gaze stability
- Head and neck exercises to improve spatial orientation
- Balance exercises to improve postural control
Vestibular rehabilitation can be effective in reducing dizziness and improving balance in people with inner ear disorders.
Medications
Medications can be used to treat inner ear dizziness by reducing nausea and vomiting, improving balance, and reducing the severity of vertigo.
Some of the medications that may be used to treat inner ear dizziness include:
- Anti-nausea medications, such as meclizine and promethazine
- Anti-vertigo medications, such as betahistine and dimenhydrinate
- Balance-enhancing medications, such as donepezil and memantine
Medications can be effective in reducing the symptoms of inner ear dizziness, but they may also have side effects, such as drowsiness, dry mouth, and constipation.
Dizziness caused by inner ear problems can be treated with medications, exercises, or surgery. For quick relief from a vertigo attack, try the Epley maneuver or other exercises to reposition the crystals in your inner ear. Learn more about how to stop vertigo attack and find effective treatments for dizziness caused by inner ear issues.
Surgery
Surgery may be an option for people with severe inner ear dizziness that does not respond to other treatments.
The type of surgery that is performed will depend on the underlying cause of the dizziness.
Some of the surgical procedures that may be used to treat inner ear dizziness include:
- Labyrinthine ablation: This procedure involves destroying the labyrinth, which is the part of the inner ear that is responsible for balance.
- Vestibular nerve section: This procedure involves cutting the vestibular nerve, which is the nerve that carries balance information from the inner ear to the brain.
- Cochlear implantation: This procedure involves implanting a device into the cochlea, which is the part of the inner ear that is responsible for hearing.
Surgery can be effective in reducing the symptoms of inner ear dizziness, but it is also a major procedure with potential risks, such as hearing loss and facial paralysis.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing Inner Ear Dizziness
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve the management of dizziness caused by inner ear problems. These modifications aim to reduce the frequency and severity of dizzy episodes, enhancing overall well-being.
Dietary Changes
Dietary modifications can positively impact inner ear health. Reducing salt intake helps regulate fluid balance, minimizing fluid retention that can contribute to dizziness. Additionally, avoiding caffeine and alcohol is beneficial as these substances can worsen dizziness symptoms.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the vestibular system, which plays a crucial role in balance. Exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga can improve balance and coordination, reducing the likelihood of dizziness.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate dizziness symptoms. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help manage stress levels and minimize their impact on dizziness.
Adequate Sleep
Getting sufficient sleep is essential for overall health, including inner ear function. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow the body to rest and repair itself.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking damages blood vessels and restricts blood flow, negatively affecting inner ear health. Quitting smoking can improve circulation and reduce the risk of dizziness.
Avoid Sudden Movements
Sudden head movements, like quickly turning or bending over, can trigger dizziness. Practicing slow and controlled movements can help prevent these episodes.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall health, including inner ear function. Drinking plenty of fluids helps maintain fluid balance and reduces the risk of dehydration, which can contribute to dizziness.
Rehabilitation and Exercise for Inner Ear Dizziness: Treatment For Dizziness Caused By Inner Ear
Rehabilitation and exercise play a crucial role in managing dizziness caused by inner ear issues. These interventions aim to improve balance and reduce symptoms by strengthening the vestibular system, which is responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation.
Rehabilitation typically involves a combination of exercises and techniques designed to stimulate the vestibular system and retrain the brain to compensate for the inner ear dysfunction.
Balance Exercises
- Standing on one leg with eyes open and closed
- Walking heel-to-toe in a straight line
- Performing balance drills with a balance board or wobble cushion
Vestibular Exercises
- Head and eye exercises: Moving the head and eyes in different directions to stimulate the vestibular system
- Epley maneuver: A specific set of head movements used to reposition displaced calcium crystals in the inner ear
- Brandt-Daroff exercises: A series of head and body movements performed to reduce dizziness
Other Techniques
- Tai chi: A mind-body exercise that improves balance and coordination
- Yoga: Certain yoga poses can help strengthen the core and improve balance
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can provide personalized exercises and techniques to improve balance and reduce dizziness
Medications for Inner Ear Dizziness
Medications play a crucial role in managing dizziness caused by inner ear disorders. These medications work by targeting different mechanisms responsible for causing dizziness and improving balance.
Anti-Nausea Medications
Anti-nausea medications, such as meclizine, promethazine, and scopolamine, help suppress nausea and vomiting, which can accompany dizziness. These medications work by blocking the action of certain neurotransmitters in the brain and inner ear that contribute to nausea and vomiting.
- Meclizine:Taken orally, it is effective in reducing dizziness and nausea associated with motion sickness and inner ear disorders.
- Promethazine:This medication is administered orally or via injection and is commonly used to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting.
- Scopolamine:Available as a patch or tablet, scopolamine is effective in preventing motion sickness and reducing dizziness.
Vestibular Suppressants
Vestibular suppressants, such as benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, lorazepam) and anticholinergics (e.g., scopolamine, trihexyphenidyl), work by reducing the activity of the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation.
- Benzodiazepines:These medications are commonly used to treat anxiety and seizures. They can also help reduce dizziness by suppressing the vestibular system.
- Anticholinergics:These medications block the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in the vestibular system. By reducing acetylcholine activity, anticholinergics can help alleviate dizziness.
Other Medications
Other medications, such as diuretics and corticosteroids, may be used in specific cases to address underlying conditions contributing to inner ear dizziness.
- Diuretics:These medications help remove excess fluid from the body, which can reduce pressure on the inner ear and alleviate dizziness.
- Corticosteroids:These medications can reduce inflammation in the inner ear, which may contribute to dizziness.
Dosage, Administration, and Side Effects:The dosage, administration, and potential side effects of these medications vary depending on the specific medication and the individual patient. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate medication and dosage for your specific condition.
Surgical Interventions for Inner Ear Dizziness
In severe cases of inner ear dizziness that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgical interventions may be considered. These surgeries aim to correct the underlying cause of the dizziness, such as a tumor or a damaged nerve.
The decision to undergo surgery is made on a case-by-case basis, after carefully weighing the risks and potential benefits. The type of surgery performed depends on the specific underlying cause of the dizziness.
Surgical Procedures for Inner Ear Dizziness
- Vestibular nerve section:This surgery involves cutting the vestibular nerve, which transmits signals from the inner ear to the brain. It is typically performed to treat severe, debilitating dizziness caused by a damaged vestibular nerve.
- Labyrinthectomy:This surgery involves removing the inner ear structures responsible for balance, including the cochlea and the semicircular canals. It is typically performed to treat severe, intractable dizziness caused by a damaged inner ear.
- Cochlear implantation:This surgery involves implanting a small electronic device into the cochlea to restore hearing. It can also be used to treat dizziness caused by a damaged cochlea.
Surgical interventions for inner ear dizziness are complex procedures that require specialized expertise. They should only be performed by experienced surgeons in specialized centers.
Final Conclusion

Managing dizziness caused by inner ear issues requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the underlying medical conditions, utilizing appropriate diagnostic procedures, and implementing effective treatment strategies, you can effectively alleviate symptoms and improve your balance. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right guidance and support, you can reclaim your stability and live a fulfilling life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/causes-of-vertigo-1298945-color-V13-614e9f9446fe4596bd4180958509cc61.png?w=1500&resize=1500,1000&ssl=1)