The aquaponics farming system emerges as a captivating concept, intertwining the cultivation of aquatic life and plant life in a mutually beneficial dance. This innovative approach to agriculture offers a myriad of advantages, promising increased crop yield, reduced water consumption, and improved water quality.
Within an aquaponics system, fish and plants coexist harmoniously, each playing a vital role in the other’s well-being. The fish provide nutrient-rich water for the plants, while the plants purify the water for the fish. This symbiotic relationship creates a sustainable and efficient ecosystem that mimics nature’s own processes.
Aquaponics System Overview
Aquaponics is a sustainable food production system that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (plant cultivation without soil). The key principle behind aquaponics is the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants.
Fish and Plant Symbiosis
Fish waste, rich in ammonia, provides nutrients for plants. Plants absorb the ammonia and other nutrients from the water, filtering it and making it suitable for the fish. In turn, the fish provide carbon dioxide, which is essential for plant photosynthesis.
This closed-loop system allows both fish and plants to thrive in a mutually beneficial environment.
Components of an Aquaponics System
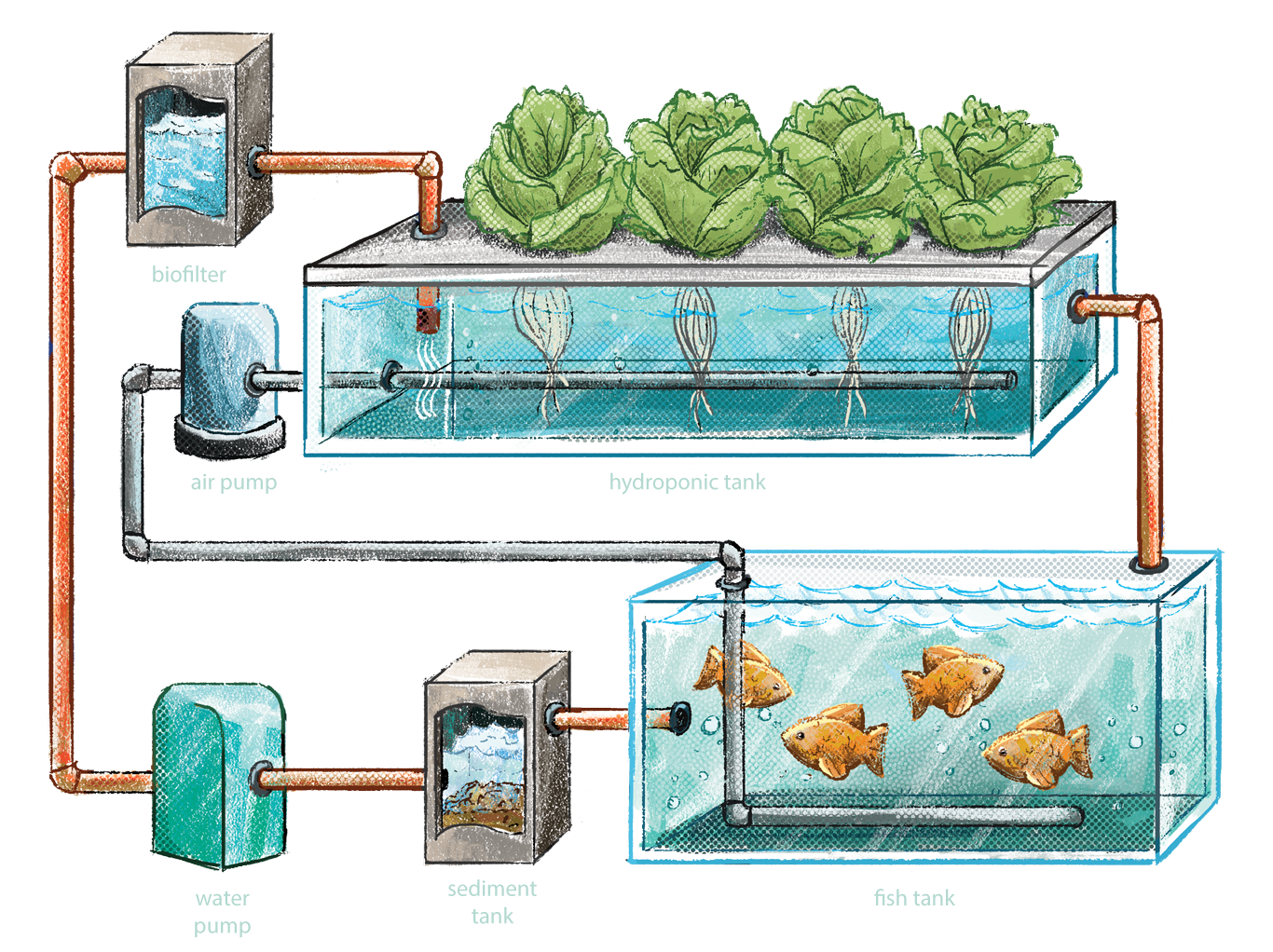
An aquaponics system is a self-sustaining ecosystem that combines aquaculture (the raising of fish) with hydroponics (the growing of plants in water). The system relies on the natural cycling of nutrients between the fish and plants to create a balanced and productive environment.
The main components of an aquaponics system are:
Fish Tanks
The fish tanks are where the fish are raised. The tanks can be made of a variety of materials, including plastic, fiberglass, or concrete. The tanks should be large enough to provide the fish with plenty of space to swim and grow.
Grow Beds
The grow beds are where the plants are grown. The grow beds can be made of a variety of materials, including gravel, sand, or expanded clay pebbles. The grow beds should be large enough to provide the plants with plenty of space to grow.
Water Filtration System
The water filtration system is responsible for cleaning the water in the system. The filtration system can be a simple as a gravel filter or as complex as a multi-stage filtration system. The filtration system should be sized to handle the volume of water in the system.
Pumps
The pumps are responsible for circulating the water in the system. The pumps should be sized to handle the volume of water in the system and the height of the water column.
Nutrient Monitoring Equipment, Aquaponics farming system
The nutrient monitoring equipment is used to monitor the levels of nutrients in the water. The nutrient monitoring equipment can be a simple as a test kit or as complex as a continuous monitoring system. The nutrient monitoring equipment should be used to ensure that the plants are getting the nutrients they need.
Types of Aquaponics Systems: Aquaponics Farming System
Aquaponics systems can be classified into various types based on their design and operational principles. Each type offers unique advantages and considerations for different farming setups and requirements.
Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS)
RAS are closed-loop systems where water is recirculated continuously through the aquaculture and plant components. The water is treated and filtered to maintain optimal conditions for both fish and plants. RAS systems are often used for commercial aquaponics operations due to their high efficiency and water conservation.
Media-Based Systems
In media-based systems, plants are grown in a solid growth medium, such as gravel, expanded clay, or rockwool. The water containing nutrients from the aquaculture component is periodically pumped or dripped over the growth medium, allowing the plants to absorb nutrients directly from the water.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Systems
NFT systems are characterized by a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over the roots of plants. The water is constantly recirculated and oxygenated to provide optimal conditions for plant growth. NFT systems are known for their high productivity and space efficiency.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Systems
DWC systems are similar to NFT systems, but the plants are suspended directly in a deep reservoir of nutrient-rich water. The roots of the plants are constantly submerged in the water, allowing for continuous nutrient uptake. DWC systems are often used for growing leafy greens and herbs.
Benefits of Aquaponics Farming
Aquaponics farming offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive and sustainable agricultural practice. Let’s explore these benefits in detail:
Increased Crop Yield
Aquaponics systems can significantly increase crop yields compared to traditional farming methods. The integration of fish and plants creates a mutually beneficial ecosystem where plants receive nutrient-rich water from the fish waste, promoting their growth and productivity. The closed-loop system allows for efficient water and nutrient utilization, maximizing plant yield.
Reduced Water Consumption
Aquaponics systems are highly water-efficient, consuming up to 90% less water than conventional agriculture. The recirculating nature of the system allows water to be reused multiple times, reducing the need for external water sources. This is particularly advantageous in regions with water scarcity or during drought conditions.
Improved Water Quality
Aquaponics systems play a vital role in improving water quality. The plants act as natural filters, removing excess nutrients, heavy metals, and other pollutants from the water. The water is then returned to the fish tanks, providing a clean and healthy environment for the fish.
This closed-loop system ensures water quality is maintained and reduces the risk of waterborne diseases.
Reduced Fertilizer Use
In aquaponics, the fish waste provides a natural source of nutrients for the plants, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers. This not only reduces production costs but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with fertilizer runoff and leaching. The nutrient-rich water from the fish tanks ensures plants receive a balanced and continuous supply of essential nutrients.
Year-Round Production
Aquaponics systems can operate year-round, regardless of external weather conditions. The controlled environment of greenhouses or indoor facilities allows for optimal growing conditions, enabling the production of fresh produce throughout the year. This provides a consistent supply of high-quality food and reduces reliance on seasonal availability.
Challenges of Aquaponics Farming
/GettyImages-142873284-7afec7706c2a4997841bde2792c7ff6b.jpg)
Aquaponics farming, despite its numerous advantages, presents several challenges that farmers must be aware of and address effectively to ensure a successful operation.
Initial Investment Costs
Establishing an aquaponics system requires a substantial initial investment in infrastructure, including tanks, pumps, filters, and grow beds. These costs can vary depending on the scale and complexity of the system.
Disease Management
Aquaponics systems are susceptible to various diseases that can affect both fish and plants. Maintaining optimal water quality and implementing proper biosecurity measures are crucial to prevent disease outbreaks and minimize their impact on the system.
Water Quality Control
Water quality is paramount in aquaponics, as it affects both fish health and plant growth. Managing water parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrite, and dissolved oxygen is essential to maintain a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
Technical Complexity
Aquaponics systems require technical expertise to operate and maintain effectively. Farmers must have a good understanding of both aquaculture and hydroponics to ensure the proper functioning of the system.
Applications of Aquaponics Farming
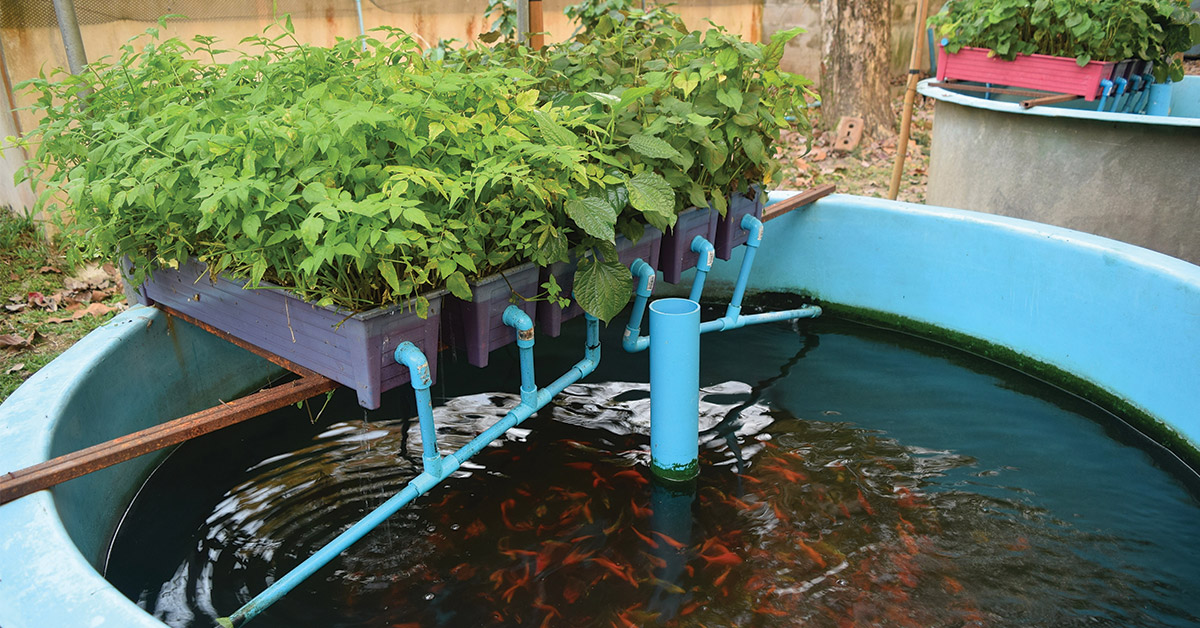

Aquaponics farming offers diverse applications, ranging from commercial food production to educational initiatives.
Aquaponics farming finds commercial application in large-scale production of fish and vegetables. Commercial aquaponics systems are designed to maximize efficiency and yield, providing a sustainable source of fresh, high-quality food for local markets and beyond.
Backyard Gardening
Aquaponics systems can be scaled down for backyard gardening, allowing individuals and families to grow their own food in a space-efficient and sustainable manner. Backyard aquaponics systems can be customized to suit specific needs and preferences, offering a fun and educational way to cultivate fresh produce.
Educational Purposes
Aquaponics systems are valuable tools for educational institutions, providing students with hands-on experience in agriculture, biology, and environmental science. Aquaponics demonstrations and workshops can teach students about the principles of sustainable food production, water conservation, and the interconnectedness of living organisms.
Research and Development
Aquaponics systems are used in research and development initiatives to explore new techniques and technologies for optimizing food production. Research efforts focus on improving water filtration, nutrient management, fish health, and plant growth strategies, with the aim of advancing the field of aquaponics and enhancing its sustainability.
Sustainability of Aquaponics Farming
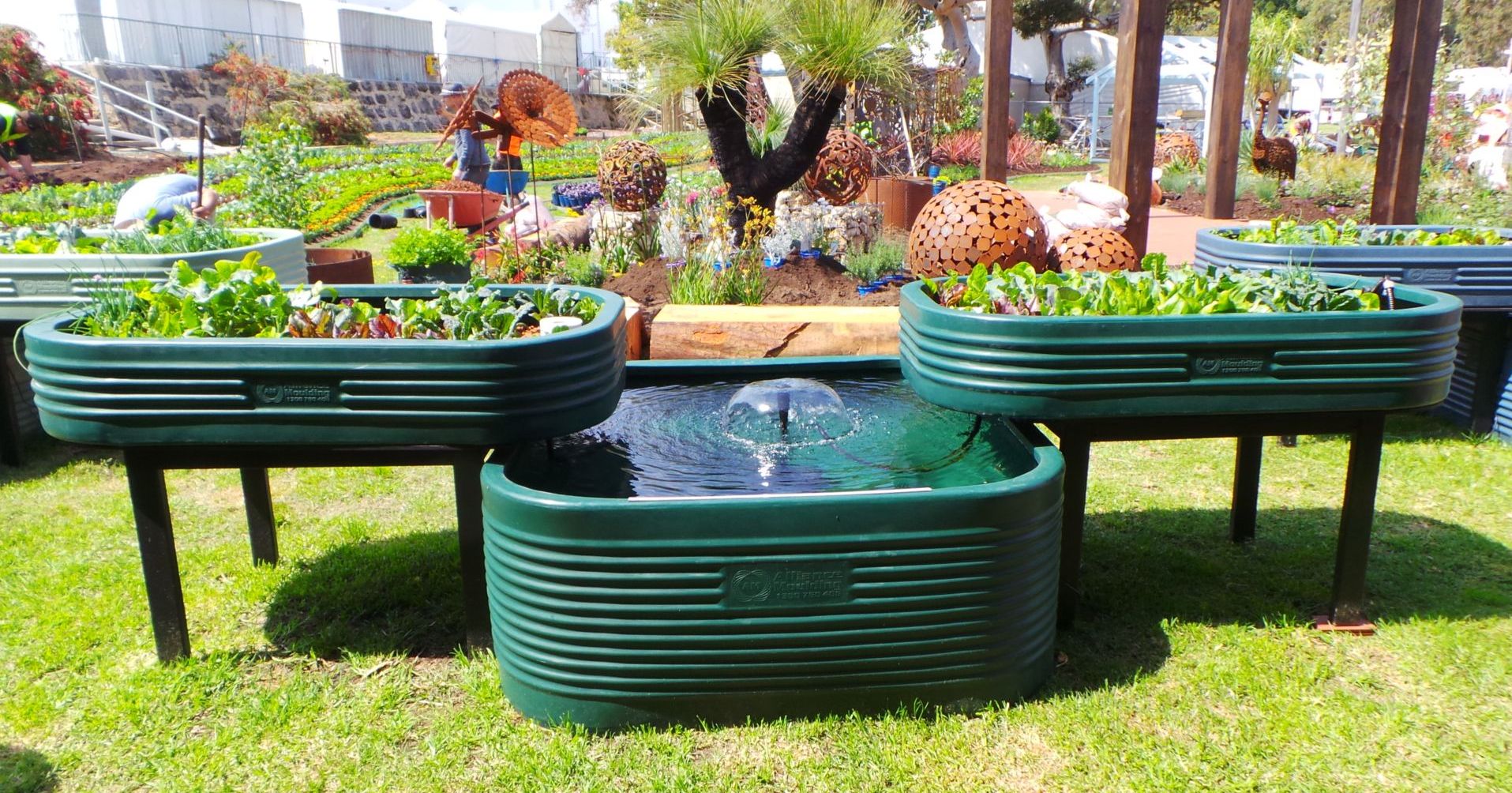

Aquaponics farming offers significant sustainability benefits by promoting environmentally friendly practices, efficient resource utilization, and local food production.
In the realm of sustainable agriculture, the aquaponics farming system stands out as a brilliant fusion of aquaculture and hydroponics. By harnessing the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, this system provides a thriving environment for both. As you delve into the various fish farming methods here , you’ll gain insights into the techniques used to optimize fish production in aquaponics.
Understanding these methods is crucial for maintaining a balanced ecosystem within the system and maximizing its efficiency.
One of the primary sustainability benefits of aquaponics is its reduced environmental impact. By combining aquaculture and hydroponics, aquaponics eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, reducing water pollution and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
Efficient Use of Resources
Aquaponics systems optimize resource utilization by recycling water and nutrients. The water used in fish tanks is naturally fertilized by fish waste, which provides nutrients for plants grown in the hydroponic component. This closed-loop system minimizes water consumption and nutrient loss, conserving valuable resources.
Local Food Production
Aquaponics farming enables local food production, reducing transportation costs and emissions associated with importing produce. By establishing aquaponics systems in urban or peri-urban areas, communities can increase food security and access fresh, locally grown produce.
Case Studies of Successful Aquaponics Farms

Aquaponics farming has gained significant traction worldwide, with numerous successful farms showcasing the potential of this sustainable and efficient food production system. These case studies highlight key factors contributing to their success and provide valuable insights for aspiring aquaponics entrepreneurs.
One prominent example is the Ecoponics farm in South Africa. Established in 2011, Ecoponics has grown into a thriving commercial operation that produces a variety of vegetables and fish for local markets. The farm’s success is attributed to its innovative use of technology, such as automated feeding systems and water quality monitoring, which optimizes production and reduces labor costs.
Key Factors Contributing to Success
- Optimized Water Management:Efficient water management is crucial for maintaining a balanced ecosystem in aquaponics systems. Successful farms prioritize water filtration, aeration, and nutrient monitoring to ensure optimal conditions for both plants and fish.
- Healthy Fish Stock:The health and vitality of fish are essential for a successful aquaponics system. Farms that prioritize fish health through proper nutrition, disease prevention, and water quality management ensure a stable and productive ecosystem.
- Diverse Plant Selection:Successful aquaponics farms often cultivate a variety of plant species to maximize production and nutritional value. By selecting plants with varying nutrient requirements and growth rates, farmers can optimize resource utilization and produce a range of marketable products.
- Market Access and Marketing:Establishing strong market connections and effective marketing strategies is crucial for the commercial success of aquaponics farms. Successful farms focus on building relationships with local restaurants, retailers, and consumers to promote their products and ensure a steady income stream.
- Financial Management:Aquaponics farming requires careful financial planning and management to ensure profitability. Successful farms maintain accurate records, control expenses, and explore innovative revenue streams to sustain their operations.
Epilogue
Aquaponics farming presents a promising solution to the challenges of modern agriculture. Its sustainability, efficiency, and versatility make it an attractive option for commercial food production, backyard gardening, and educational purposes. As research and development continue to advance this field, the potential of aquaponics farming to transform the way we produce food is limitless.
FAQ Explained
What are the key components of an aquaponics system?
An aquaponics system typically includes fish tanks, grow beds, a water filtration system, pumps, and nutrient monitoring equipment.
What are the different types of aquaponics systems?
There are several types of aquaponics systems, including recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), media-based systems, nutrient film technique (NFT) systems, and deep water culture (DWC) systems.
What are the benefits of aquaponics farming?
Aquaponics farming offers numerous benefits, such as increased crop yield, reduced water consumption, improved water quality, reduced fertilizer use, and year-round production.
